Choosing the Right Emulsifier(s) for Stable Emulsification
- PhytoAxia
- Nov 22, 2025
- 3 min read
Formulating for beginners can be a daunting task. Emulsions are sensitive to many factors; even a small mistake can result in unstable formulations. Creating stable formulations depends on the formula, the compatibility of ingredients, choice of emulsifiers, and even seemingly trivial details such as the weight of the cool-down phase. For example, when I first started creating formulations, I followed textbook instructions for successful formulating. However, to my dismay, the final product would often separate. I soon realized that the compatibility of oil phase ingredients also played a crucial role. In this blog, we use the term "all things being equal" to emphasize that assuming there are no other influencing factors (such as heat-sensitivity, ingredient compatibility, or correct ingredient choice), the following method of determining the emulsifier composition of a formulation will result in physically stable formulations.
The Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) System
The HLB system is a formalized tool that helps determine the correct amount and combination of emulsifiers required for successfully mixing oil and water components in emulsions. Developed, refined, and presented through a series of papers by William Griffin (1949, 1964, & 1955), the system was a guiding mechanism for the correct use of surfactants. Although his earlier work focused on broadly defined surfactant classes of materials (detergents, emulsifiers, wetting agents, suspending agents, solubilizers, foaming agents, among others), it is now extensively used as a tool to determine emulsifier combinations with the correct HLB results in physically stable emulsions.
Molecules in emulsifiers are composed of a water-loving (hydrophilic) head and an oil-loving (lipophilic) tail. The relative size of the head to the tail determines the behavior of the emulsifier. To formalize this behavior, the HLB system assigns numerical values between 0 and 20 to emulsifiers depending on the relative size of the molecule head to the tail. Emulsifiers where the head is significantly larger than the tail are classified as water-loving or hydrophilic, whereas those with relatively larger tails are classified as oil-loving. The HLB system assigns higher values to hydrophilic emulsifiers and lower values to emulsifiers with lipophilic behavior.
High HLB (Hydrophilic) Emulsifiers:
The hydrophilic emulsifiers class is assigned HLB values between 7 and 20. Within this class, there are sub-categories depending on their water solubility properties. Emulsifiers close to 7 are considered water-dispersible and become increasingly water-soluble with higher assigned HLB values.
High HLB Sub-Categories:
7-9 : Wetting and spreading agents
8-18: Oil-in-water (hydrophilic) emulsifiers
13-15: Detergents
15 >: Solubilizers.
The graph below depicts the hydrophilic emulsifiers in our store and their associated HLB values.

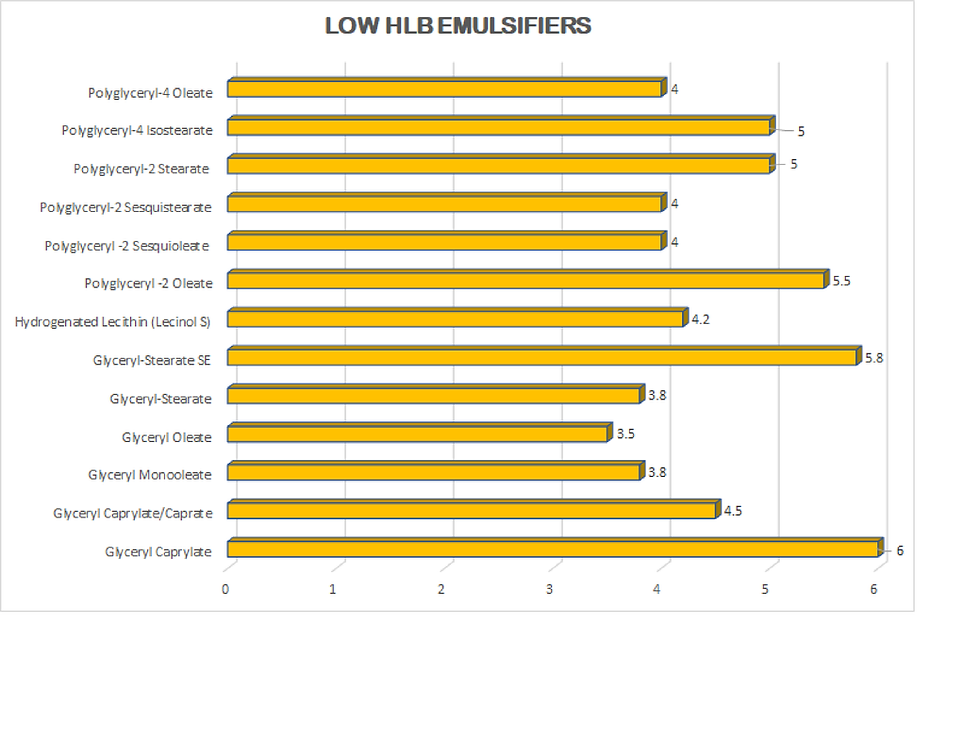
Low HLB Emulsifiers
Low HLB water-in-oil emulsifiers are a special class of emulsifiers that allow for the incorporation of water components into oil-heavy formulations. The lipophilic class of emulsifiers is assigned HLB values between 0 and 6, with sub-categories defined according to their behavioral characteristics.
Low HLB Sub-Categories:
2-3 Anti-foaming agents
3-6 Water-in-Oil Emulsifiers
The use of high polymetric weight emulsifiers is recommended for oil-heavy formulations to achieve stable emulsification. The graph below depicts the lipophilic emulsifiers in our store and their associated HLB values.
Required HLB for Oils
A key component of determining emulsifier requirements is knowing the required HLB for the oils in a formula. The required HLB for an oil is the HLB of the emulsifier needed to successfully incorporate a specific oil into an emulsion. For example, the required HLB of emulsifiers to successfully incorporate almond oil into an emulsion is 6. The table below shows the HLB requirements of common oils and fatty acids used in formulations.
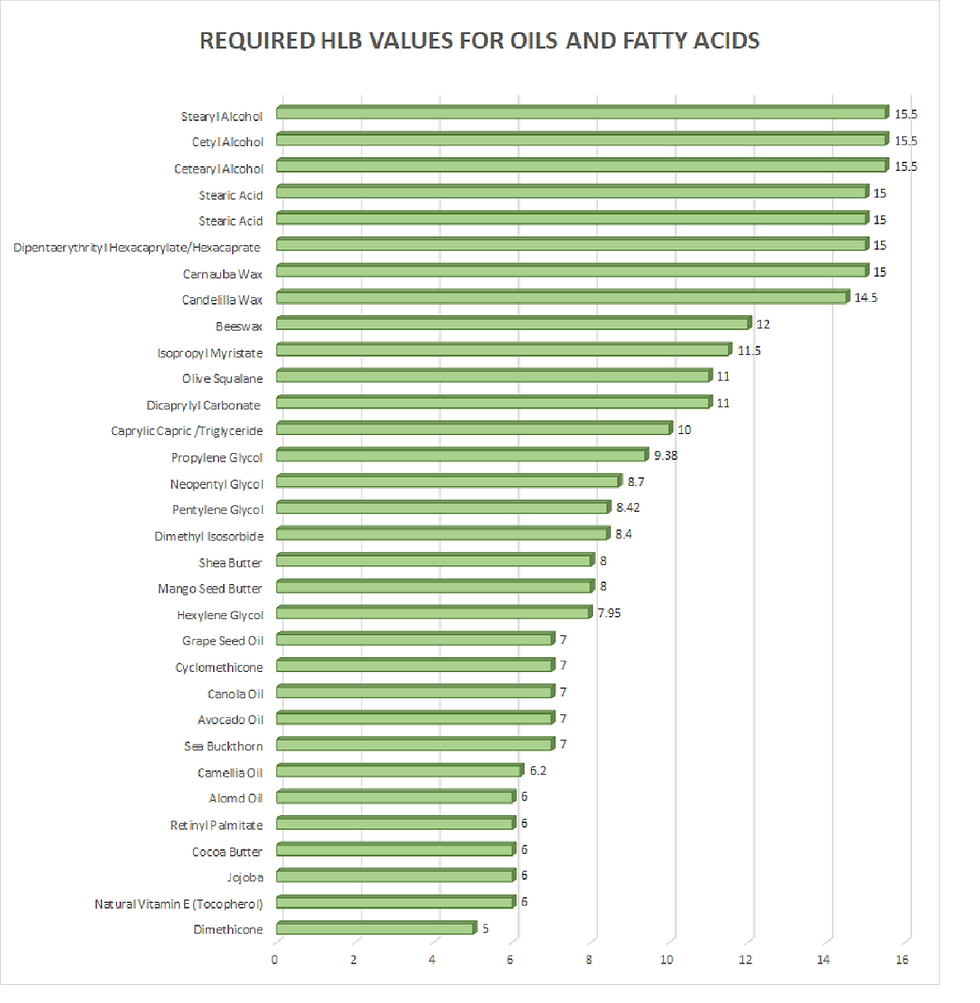
Most often, the oil phase contains more than one oil and fat component. It is common for the oil phase to contain oils, fatty acids, and other agents. In this case, it is necessary to determine the HLB of the oil phase before deciding which emulsifiers and proportions to use in the formulation. The HLB requirement of the oil phase is the weighted HLB of the oil phase components.
Optimal Emulsifier Combination
For illustrative purposes, assume that the formula for an emulsion is structured according to the table below.

The following section provides a step-by-step guide to determining the optimal emulsifier combination.


Source(s)


Comments